Managing Credit Risk, Gen AI Style

Generative AI is revolutionising credit risk management – enhancing efficiency, promoting personalisation and automating tasks across the credit lifecycle – helping financial institutions optimise resources and decision-making. However, scaling requires addressing governance, talent gaps, and environmental concerns. Institutions that effectively adopt Gen AI will gain a competitive edge and drive innovation in the sector.
Generative AI (Gen AI), with its ability to analyse and produce content in natural language, has emerged as a transformative force in many industries, perhaps few as much as in global credit risk management. Traditionally conservative in adopting emerging technologies, financial institutions are now integrating Gen AI to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and personalise customer interactions. A recent report from McKinsey’s Risk & Resilience Practice provides an in-depth look at how generative AI is reshaping the credit risk landscape, from client engagement to portfolio management.
The Role of Generative AI in Credit Risk
Gen AI leverages large language models (LLMs) to process and analyse unstructured data, simulate natural language, and create structured outputs. This versatility makes it a powerful tool across the credit risk lifecycle. According to McKinsey, 80% of surveyed credit risk organisations expect to implement Gen AI technologies within the next two years. Current use cases focus on operational improvements and addressing specific pain points in credit risk processes:
- Client Engagement:Gen AI enables hyper-personalised services by analysing customer profiles and activity histories. It can draft individualised communications, summarise interactions, and suggest next steps for relationship managers. For example, virtual assistants powered by Gen AI can guide customers through product selection and provide expert-like advice on credit options.
- Underwriting and Credit Decision Processes:In underwriting, Gen AI reviews documents, flags policy violations, and identifies missing information. By automating data collection, analysis, and drafting of credit memos, Gen AI accelerates decision-making. McKinsey notes that agent-based AI systems can independently calculate ratios, compare them to thresholds, and generate comprehensive reports in plain language, reducing manual intervention.
- Portfolio Monitoring and Early Warning Systems:Portfolio managers can benefit from Gen AI’s ability to draft performance and risk reports, propose optimisation strategies, and enhance early-warning systems. By processing real-time unstructured data like news or market updates, Gen AI can identify potential risks and suggest preventive measures for specific borrower segments.
- Collections and Customer Assistance:For delinquent accounts, Gen AI drafts personalised outreach messages, proposes restructuring options, and guides customers through repayment plans. It also provides post-interaction analysis to improve agent performance, ensuring empathetic and efficient customer service.
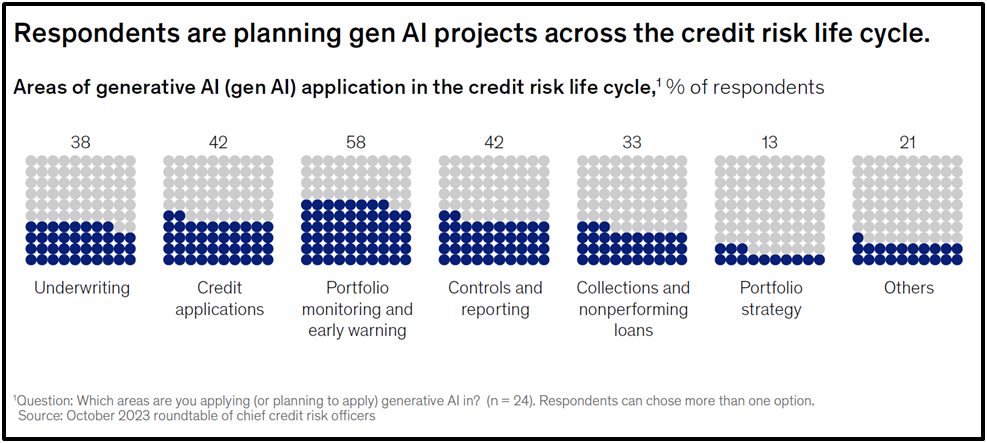
Image: Generative AI applications in credit life cycle; Source: McKinsey & Co.
Early adopters have reported significant efficiency improvements with Gen AI. A McKinsey-cited case involves a bank using Gen AI to prepopulate climate risk questionnaires, reducing the completion time from two hours to 15 minutes while maintaining a 90% accuracy rate. Similarly, credit memo drafting tools have improved the consistency and speed of credit evaluations, freeing up resources for strategic tasks.
The programming simplicity of Gen AI, relying on natural language rather than complex coding, further accelerates adoption. Systems can integrate multiple agent layers to execute intricate tasks, ensuring accuracy and minimising errors like hallucinations.
While Gen AI holds immense promise, financial institutions face challenges in deploying it at scale. According to McKinsey, 75% of surveyed executives highlighted governance risks, including:
- Fairness and Bias:Algorithms may unintentionally perpetuate biases, leading to discriminatory outcomes.
- Privacy Concerns: Using personal or sensitive data for training models raises ethical and legal issues.
- Intellectual Property Violations:Improperly sourced training data may infringe on copyrights.
- Performance Reliability: Gen AI models can produce inaccurate or misleading outputs, necessitating robust validation systems.
Other hurdles include a lack of skilled talent, fragmented approaches to defining use cases, and difficulty quantifying the value of Gen AI implementations. Additionally, environmental concerns around AI’s energy-intensive operations add to the governance complexity.
To overcome these challenges, McKinsey recommends adopting a structured approach to integrating Gen AI into credit risk operations. Key practices include:
- Developing an AI Roadmap: Align Gen AI initiatives with the organisation’s strategic objectives, outlining timelines and necessary resources.
- Establishing Governance Frameworks:Address risks related to fairness, privacy, and performance through rigorous oversight and standardised protocols.
- Investing in Talent and Training: Build cross-functional teams with expertise in AI, natural language processing, and regulatory compliance.
- Leveraging Modular Architectures:Design adaptable systems that can integrate with existing workflows and scale as needed.
- Utilising Pre-Trained Models and Open-Source Tools: Accelerate deployment by building on foundational AI models and reusable components.
For instance, modular architectures enable parallel development, allowing firms to quickly test and deploy solutions. Open-source libraries further simplify implementation, reducing time-to-market for Gen AI applications.
As Gen AI matures, its applications in credit risk are expected to expand beyond current use cases. Emerging possibilities include:
- Dynamic Risk Profiling: Real-time adjustments to borrower risk scores based on evolving market conditions.
- Integrated Fraud Detection: Enhanced pattern recognition to identify and mitigate fraudulent activities during credit application processes.
- Customisable Loan Products: Tailored credit solutions based on comprehensive customer insights, improving access and satisfaction.
Experts emphasise Gen AI’s transformative potential lies in its ability to integrate seamlessly with other technologies, such as machine learning and blockchain. This convergence could enable end-to-end automation of credit risk processes, setting new standards for speed, accuracy, and customer experience.





